priority time capacity management
This section is focused on various aspects of priority, time, and capacity management
There is no one-size-fits-all solution, it depends on the nature of the work you are doing
Our scenario/story video is all about "When someone adds to your workload"
What you prioritize is arguably just as important as the results you produce
The Art of Prioritization
Why?
- Structuring what you work on and when is beneficial and essential for success
- It also signals to your team and stakeholders that you're focusing on the right things
Understanding prioritization
- Prioritization is both a task management tool and a strategic mindset to help you achieve the best outcomes with the resources and time available
Strategies for prioritization - WSJF (Weighted Shortest Job First)
- Break down the work
- Identify the level of effort (time required)
- Determine the level of value (impact or benefit)
- Prioritize tasks that deliver the highest value in the shortest amount of time
WSJF - Illustration
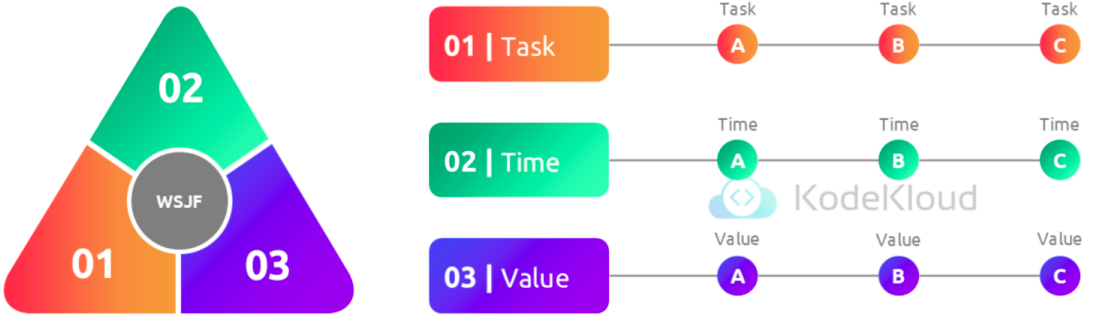
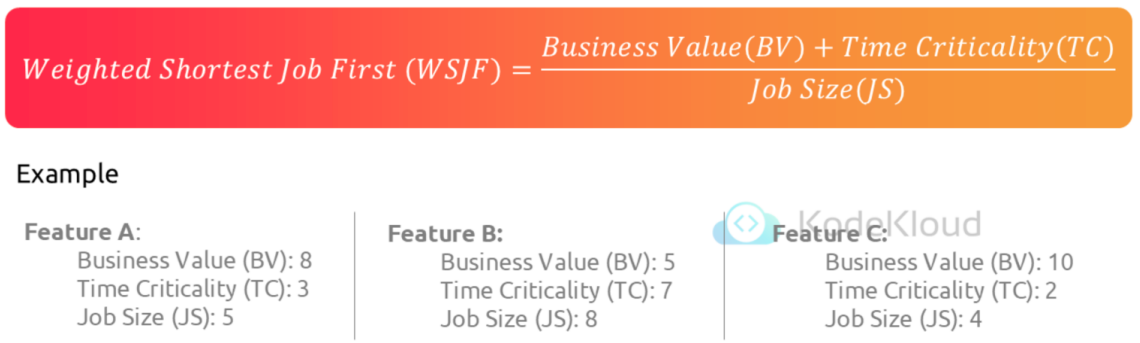
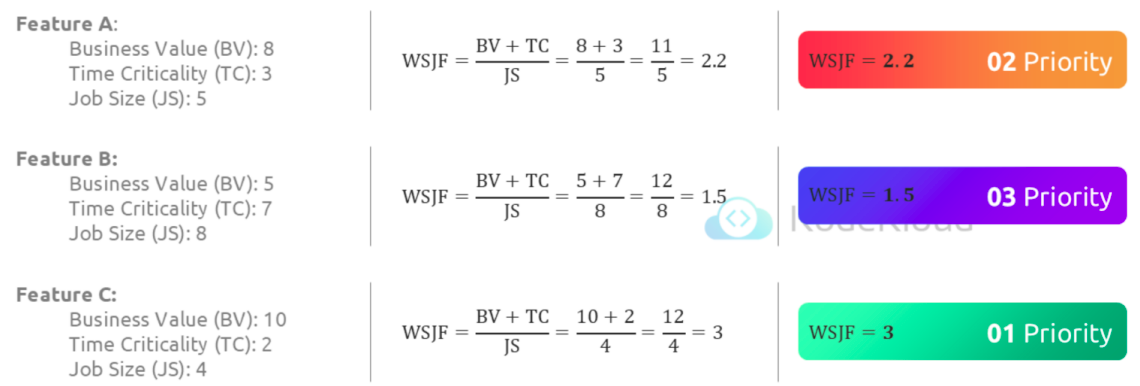
Strategies for prioritization - Pareto
- This method is based on the principle that 80% of results often come from 20% of efforts
- Focus on identifying the small number of tasks that will generate the most significant results
- Helps reduce wasted effort and optimize focus
Strategies for prioritization - FIFO
- Prioritize tasks in the order they arrive - first task received is the first task completed
- Useful in support queues or environments where fairness and order are key
- Works well when all tasks are relatively equal in urgency and impact
Strategies for prioritization - Eisenhower
- Categorizes tasks based on urgency and importance into four quadrants
- Urgent & Important - Do it now
- Important, Not Urgent - Schedule it
- Urgent, Not Important - Delegate it
- Not Urgent, Not Important - Eliminate it
- Great for helping individuals or teams focus on what truly matters
Strategies for prioritization - Experiment
- There's no one-size-fits-all. Experiment with different frameworks such as WSJF, Pareto, Eisenhower, or FIFO
- Choose the method or combination that best supports your goals and team workflow
Adapting to rapidly changing inputs
- In dynamic environments, priorities shift quickly. Stay adaptable by
- Re-evaluating tasks regularly
- Checking alignment with strategic goals
- Using flexible tools or boards to adjust quickly
- Stay aligned while adapting to evolving realities!
Effective communication of priority changes
- Communicating changes in priorities is just as important as setting them
- Changing a priority means changing an agreement and failure to inform the stakeholders breaks that agreement
- Always clarify the why behind changes to maintain trust and alignment
Project work vs. interrupt-driven work
- Mixing these two types of work can be extremely challenging. To manage effectively
- Keep workflows separate where possible
- Block time specifically for deep-focus project work
- Schedule windows for handling interrupts (e.g., support issues)
- Use rotating team shifts for support-heavy environments
- Clearly communicate capacity limits with stakeholders
- Example
- Separated workflows: Support issues and project tasks are managed in different Jira boards to reduce context-switching
- Time blocking: Mornings (e.g., 9 AM - 12 PM) are reserved exclusively for deep-focus project work, with Slack notifications muted
- Interrupt windows: Afternoons (e.g., 2 PM - 4 PM) are dedicated to addressing support tickets, keeping reactive work contained
- Rotating on-call shifts: The team implements a rotation so only one person handles interrupts at a time, giving others space for long-term work
- Clear communication: The engineer proactively sets expectations with stakeholders, explaining that project progress depends on minimizing support duties
The power of visualizing work
- Visualization helps teams and individuals understand workload, status, and blockers
- To do → In progress → Completed
Intersection of prioritization, time management, and capacity planning
- Prioritization helps determine what to work on
- Time Management helps schedule when to work on it
- Capacity Planning ensures how much you can take on without overloading
- These elements work together to ensure focus, efficiency, and sustainable productivity
Summary
- This section highlights the alignment created by prioritizing tasks that align with the highest and most effective business need
- Prioritization is usually done by assessing effort, time, value, and urgency
- Strategies include using the 80/20 rule from the Pareto Principle, Weighted Shortest Job First from Lean, and more
- There is an intersection between capacity, time, and priority, but the most important thing is choosing the method(s) that work best for your business need
The Science of Time Management
Why?
- Time is a non-renewable resource - how we manage it directly influences our success
Understanding time management
- In a world where every second counts, mastering time management is both a critical skill and a competitive advantage
Techniques - Parkinson's Law
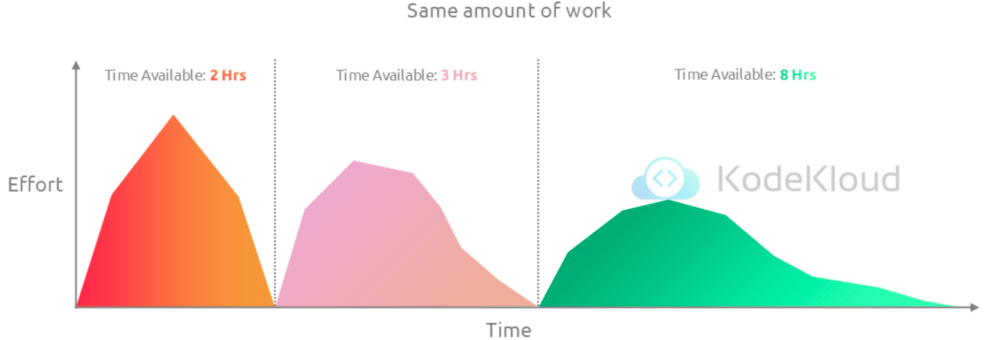
- Work expands to fill the time available for its completion
- By setting shorter deadlines, you can increase focus and efficiency
Techniques - Time Blocking
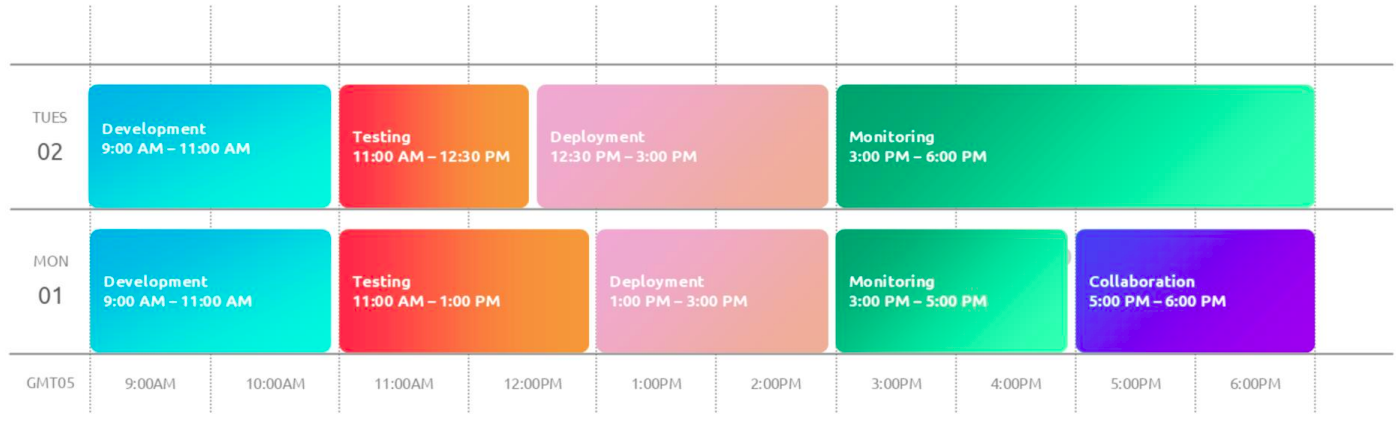
- Allocate specific time blocks for specific types of work (e.g., meetings, deep work, email)
- Helps reduce distractions and improves focus by giving each task its own space in your calendar
Techniques - Pomodoro technique
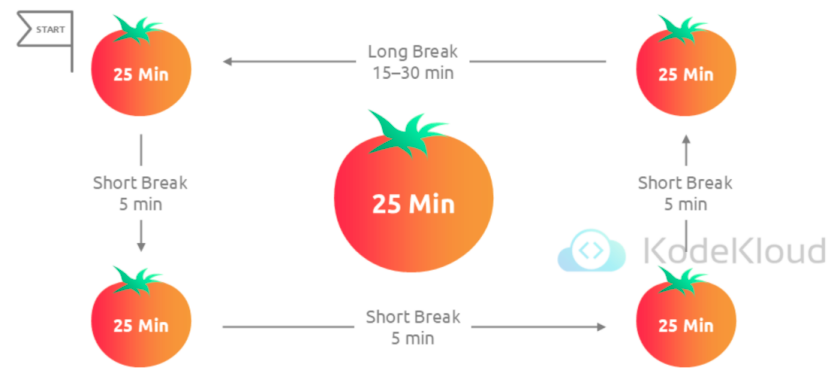
- Work in focused intervals (typically 25 minutes), followed by a 5-minute break
- After four cycles, take a longer break (15-30 minutes)
- Enhances productivity and combats mental fatigue
Tools and technologies
- Calendars and scheduling tools
- Tools: Google Calendar, Calendly, Microsoft Outlook Calendar, Apple Calendar, Doodle, etc.
- Project management servers
- Tools: ClickUp, Trello, Microsoft Planner, Notion, Doodle, etc.
- Time-tracking apps
- Tools: Toggl Track, HourStack, Timely, Memtime, TrackingTime, etc.
Common challenges and solutions
- Context switching
- Group similar tasks together (batch processing)
- Limit the number of simultaneous tasks
- Use tools like focus mode or "Do Not Disturb" to maintain flow
- Unplanned interruptions
- Block specific time windows for focused work
- Schedule time for handling ad hoc tasks or support requests
- Communicate availability clearly to your team
- Underestimating/Overestimating tasks
- Use time-tracking data to estimate more accurately
- Break tasks into smaller, measurable chunks
- Build in buffer time for unexpected delays
Summary
- Time management is critically important to almost all aspects of DevOps, IT, and Software Delivery
- Parkinson's Law, Time Blocking, and other methods were covered to understand time management concepts
- The Pomodoro technique, the Two-Minute Rule, and other techniques help with time management
- Time management is essential for prioritizing the right things for whom you work
The Magic of Capacity Planning
Why?
- Capacity planning is essential both personally and professional for understanding how much we can handle at any given time
The foundation
- In environments where agility and efficiency are paramount, capacity planning becomes a key driver of success
- Assessing current resources → Forecasting future needs → Allocating resources to projects → Adjusting resources
Problem it solves
- Manages fluctuating workloads
- Prevents burnout
- Aligns team effort with organizational or project requirements
- Minimizes waste
- Maximizes outcomes
Effective capacity planning
- Understand the nature of the work and the total workload
- Assess your current capability and available resources
- Clarify all constraints (time, money, skills, tools, and availability)
- Identify potential risks and bottlenecks
Strategies
- Regular workload review timeline
- Start → Initial review → First stage review → Second stage review → Final review → End
- Historical data line graph
- Analyze past performance and capacity trends to inform future planning
- Capacity planning tools
- Leverage digital tools for forecasting, tracking, and scenario planning (e.g., Float, Resource Guru, MS Project, Smartsheet)
Benefits
- Smoother project workflows
- Higher team morale and lower stress
- Improved risk anticipation and mitigation
- More sustainable and predictable output over time
Visualization
- A picture is worth a thousand words, and in capacity planning, a visual tool can be worth even more
Summary
- Capacity planning is an essential part of connecting resources with tasks
- Capacity planning is fueled by Prioritization and sustained by time management
- Teams and individuals benefit from the consistency of sustainable and intentional ways of working
- At a minimum, understanding that capacity planning is important and how to do it is essential
Story - When Someone Adds to Your Work
Context
- You're in the middle of a well-planned DevOps sprint, resources are balanced, everyone knows what they're doing, and progress is steady
- Then, out of nowhere, someone - usually a high-priority stakeholder drops a new task on your lap and says, "This needs to go in now"
- In this particular story, a team was halfway through a two-week sprint when a last-minute regulatory task came in from a key stakeholder
- The task was high priority and couldn't wait, so the team had to figure out how to deal with it without derailing their sprint or burning out
- This situation? It's super common in DevOps and agile teams. The key is knowing how to respond with clarity, calm, and a solid plan
Actions and result
- Prioritize with intention
- Evaluate the importance, urgency, and size of the new request. Compare it against existing work. Don't just react - prioritize. Use scoring, matrices, or just a calm discussion to figure out what matters most
- You get clarity on whether the new task truly deserves to interrupt the sprint, and you avoid turning your sprint into chaos based on someone else's panic
- Plan around capacity
- Check your team's capacity, do you actually have room? If not, what can be dropped, reduced, or pushed to make room? Use charts, past performance, or just gut-checks with your team
- You avoid overloading the team, and you make room for important work without sacrificing what's already been committed or at least, not without a deliberate trade-off
- Communicate transparently
- Talk to your stakeholders, tell them what the impact of this new work is. Involve them in the decision. Ask, "What can we adjust to make this happen?" Don't keep things siloed
- Stakeholders feel involved and respected, your team gets direction without stress, and you preserve trust and alignment on both sides
- Adapt the plan, don't panic
- In the story, the team trimmed the scope of one task to make space for the new one. Then they updated their sprint board and got right back to work
- The new high-priority task got done, the team stayed focused, and the sprint goals were still achievable with some smart adjustments
- Stay systematic, not emotional
- Use structured tools, prioritization systems, capacity planning, transparent task boards to handle changes calmly and logically
- You protect your team's sanity, maintain momentum, and show leadership even when plans shift unexpectedly
Quiz
| Number | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | What is the focus of the "Understanding Time Management in DevOps" slide? | Introducing the concept of time management and its importance in DevOps |
| 2 | According to the "Core Components of Effective Capacity Planning" slide, what does capacity planning involve? | Considering factors like team skill levels and tooling capacities |
| 3 | The Pareto Principle, as described in the "Effective Strategies for Prioritization" slide, states that | 20% of tasks contribute to 80% of the results |
| 4 | According to the "Mastering the Art of Prioritization" slide, what is prioritization in the context of DevOps? | A strategic approach to achieving optimal outcomes |
| 5 | What is the most important factor when choosing a prioritization method, according to the "Effective Strategies for Prioritization" slide? | Selecting a method that achieves desired outcomes |
| 6 | What does the "Adapting to Rapidly Changing Realities" slide suggest about priorities in DevOps? | Priorities should be evaluated and adjusted daily |
| 7 | According to the "Managing Project Work vs. Interrupt-Driven Tasks" slide, what is the consequence of mixing project work and interrupt-driven tasks? | It is very hard and must be communicated |
| 8 | Which of the following is not mentioned as a key principle of prioritization in the "Understanding Prioritization" slide? | The LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle |
| 9 | What does the phrase "seeing is more than believing" refer to in the "Visual Tools in Capacity Planning" slide? | Visualizing capacity planning helps in understanding and managing work effectively |
| 10 | What does the "Unveiling the Magic of Capacity Planning" slide describe capacity planning as? | A process for determining the production capacity needed to meet changing demands |
| 11 | What is the main difference between project work and interrupt-driven tasks, as described in the "Managing Project Work vs. Interrupt-Driven Tasks" slide? | Interrupt-driven tasks are unforeseen and require immediate attention |
| 12 | What is the purpose of the "Addressing Common Time Management Challenges" slide? | To identify common time management challenges and provide strategies to overcome them |
| 13 | Which of the following is not mentioned as a tool for visualizing capacity planning in the "Visual Tools in Capacity Planning" slide? | Burndown charts |
| 14 | Which of the following is a strategy for responding to changes in the project landscape, as per the "Adapting to Rapidly Changing Realities" slide? | Encouraging open communication within the team to identify and address shifting priorities |
| 15 | According to the "Synergizing Time Management with Prioritization and Capacity Planning" slide, how does capacity planning contribute to effective time management? | Understanding the team's capacity helps in realistically scheduling and prioritizing tasks |
| 16 | What does the "Effective Communication of Priority Changes" slide emphasize about communicating changes in priorities? | The way priority changes are communicated is as important as the changes themselves |
| 17 | What does the "Synergizing Time Management with Prioritization and Capacity Planning" slide suggest about the relationship between time management, prioritization, and capacity planning? | They are deeply interconnected |
| 18 | What is the purpose of the self-assessment segment in the "Do You Already Manage Priorities and Time Well?" slide? | To help the audience gauge their current skills in priority and time management |
| 19 | What does the "Strategic Approaches to Capacity Planning" slide recommend for predicting future capacity needs? | Analyzing historical data from previous projects |
| 20 | According to the "Exploring Key Time Management Theories" slide, what does Parkinson's Law state? | Work expands to fill the time available for its completion |
| 21 | Which of the following is not listed as a benefit of capacity planning in the "Benefits of Effective Capacity Planning" slide? | Increased project budgets |
| 22 | What does the Weighted Shortest Job First (WSJF) model focus on, according to the "Effective Strategies for Prioritization" slide? | Delivering the most value in the shortest time frame |
| 23 | Which time management technique involves working in focused intervals with short breaks, as described in the "Exploring Key Time Management Theories" slide? | The Pomodoro Technique |
| 24 | According to the "Strategic Approaches to Capacity Planning" slide, what is the benefit of fostering open communication and collaboration when planning capacity? | It maintains transparency and allows for clear documentation of plans and changes |
| 25 | Which of the following is listed as a time management challenge in the "Addressing Common Time Management Challenges" slide? | Underestimating the time required for tasks |